low end tidal co2 during cpr
Eleven intubated anesthetized paralyzed dogs mean age 41 mo. On the other hand a high co2 reading.
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education
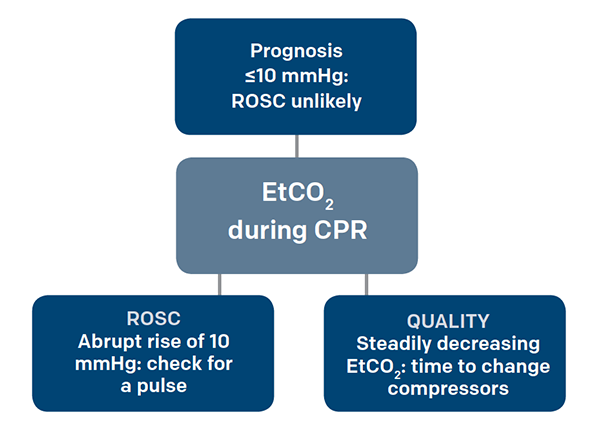
Abrupt increase in ETCO2 suggests ROSC during CPR detectable before pulse check ETCO2 at 20 minutes of CPR is prognostically useful.

. J Intensive Care Med. While doing CPR there is a sudden spike and the CO2 levels rise up this may indicate the patient has a return of spontaneous circulation ROSC. Tolin df1 billingsley al2 hallion ls2 diefenbach gj3.
End-tidal carbon dioxide concentration during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. End-tidal CO2 as a guide to successful cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Mean weight 55 kg were used.
Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al. Also called capnometry or capnography this. Levine RL Wayne MA Miller CC.
A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. N Engl J Med. Systematic review and meta-analysis of end-tidal carbon dioxide values associated with return of spontaneous circulation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Ensure proper rate approximately 100min Ensure proper depth with adequate releaserecoil of thorax 12 thorax or minimum 25. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring provides useful noninvasive information during clinical resuscitation. Here are five things you should know about waveform capnography in cardiac arrest.
A low P a CO2 level is correlated with increased risk of cerebral edema in children with DKA. Our study attempted to correlate ETCO2 to cerebral blood flow during cardiac arrest. In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide.
End-tidal carbon dioxide cannot be used to rule out severe injury in patients meeting the criteria for trauma care. Ensure proper rate approximately 100min Ensure proper depth with adequate releaserecoil of thorax 12 thorax or minimum 25 inches Persistently low EtCO. Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
What is end-tidal CO2 etCO2. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. Carbon Dioxide During the Low Flow State Initiation of CPR.
Maslow A et al. Sixteen piglets were anesthetized intubated and. Capnography continues to be an important tool in measuring expired carbon dioxide CO 2.
Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. Ornato JP Garnett AR Glauser FL.
2 USES DURING CPR 7 CONFIRM ADEQUACY OF CHEST COMPRESSIONS. 2001Monitoring end-tidal carbon dioxide during weaning from cardiopulmonary bypass in patients without significant lung disease. A number of studies have demonstrated a correlation between end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 cardiac output and return of spontaneous circulation in experimental animals and in patients undergoing closed-chest CPR.
End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detection requires air movement. Free Full Text Critical Care. An end-tidal CO2 monitor also can help monitor a patients respiratory status during different medical procedures.
A study was undertaken to determine the pattern of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 changes during asphyxia-induced cardiac arrest in a pediatric canine model. N Engl J Med 1988318607-11. Asphyxia was induced by clamping the endotracheal tube ETT and discontinuing ventilation.
Falk JL Rackow EC Weil MH. The result is a low arterial Common causes of ave U low. Crit Care Med 198513910-11.
Most recent Advanced Cardiac Life Support ACLS guidelines now recommend using capnography to ascertain the effectiveness of chest compressions and duration of cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR. Crit Care Med 198513907-9. Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed.
End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. Monitoring end-tidal carbon dioxide during weaning from cardiopulmonary bypass in patients without significant lung disease. Weil MH Bisera J Trevino RP Rackow EC.
39 Treveno RP Bisera J Weil MH Rackow EC Grundler WG. In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign. The first sign of the return of spontaneous circulation ROSC during CPR is increase in ETCO2.
During CPR chest compressions along with positive pressure ventilation restore organ perfusion and oxygenation to some extent. Based on an extensive review of available. 6r76 Within Inadequate ventilation seconds.
End-tidal carbon dioxide and outcome of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Cardiac output and end-tidal carbon dioxide. Normal value is 35-45 mmHg.
End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 is a noninvasive technique which represents the partial pressure or maximal concentration of CO2 at the end of exhalation.

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Acep Now

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

The Role Of Etco2 In Termination Of Resuscitation Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

End Tidal Co2 Etco2 By Group And By Group And Rosc A Etco2 Versus Download Scientific Diagram

The Role Of Etco2 In Termination Of Resuscitation Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

Emergency Intubations Capnography

Sar Helicopter Paramedic Practice Etco2 Measuring To Assist With Cpr Attempts Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Capnograph Note Try To Maintain Etco2 Above 10mmhg During Cpr Nurse Anesthesia Emergency Nursing Respiratory Therapy Student

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

End Tidal Co2 Guided Automated Robot Cpr System In The Pig Preliminary Communication Resuscitation

Capnography During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Current Evidence And Future Directions
